- Published on
Deploying your first serverless program in less than 10 minutes
What is Serverless?
Serverless computing is a cloud computing execution model in which the cloud provider dynamically manages the allocation of machine resources. Pricing is based on the actual amount of resources consumed by an application, rather than on pre-purchased units of capacity There are several use cases where Serverless Computing adds the advantage in terms of time to delivery and operational costs. Amazon AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions are the popular provides in the market today.
Choosing the cloud provider is upto you, for example if you are already in AWS ecosystem and using services like DynamoDB/ EC2 / Pub Sub then if make sense to use AWS Lambda. In this post i am using Google Cloud Functions to write my Hello World Serverless program.
Setting up gcloud SDK
gcloud is command-line interface tool which makes your life easy for creating/ updating/ deploying the Google Cloud services like AppEngine/ Datastore/ Cloud Functions etc,
Follow the instructions here https://cloud.google.com/sdk/downloads to download and setup gcloud SDK on your computer. Once everything ready you can check the successful installation by typing command gcloud --version then it should show something like below
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:~ karthikdivi$ gcloud --version
Google Cloud SDK 182.0.0
beta 2017.09.15
bq 2.0.27
cloud-datastore-emulator 1.3.0
core 2017.12.01
gcd-emulator v1beta3-1.0.0
gsutil 4.28
Now login to your Google Cloud account by typing command gcloud auth login this will take you to the browser where you can login with your Google Cloud account.
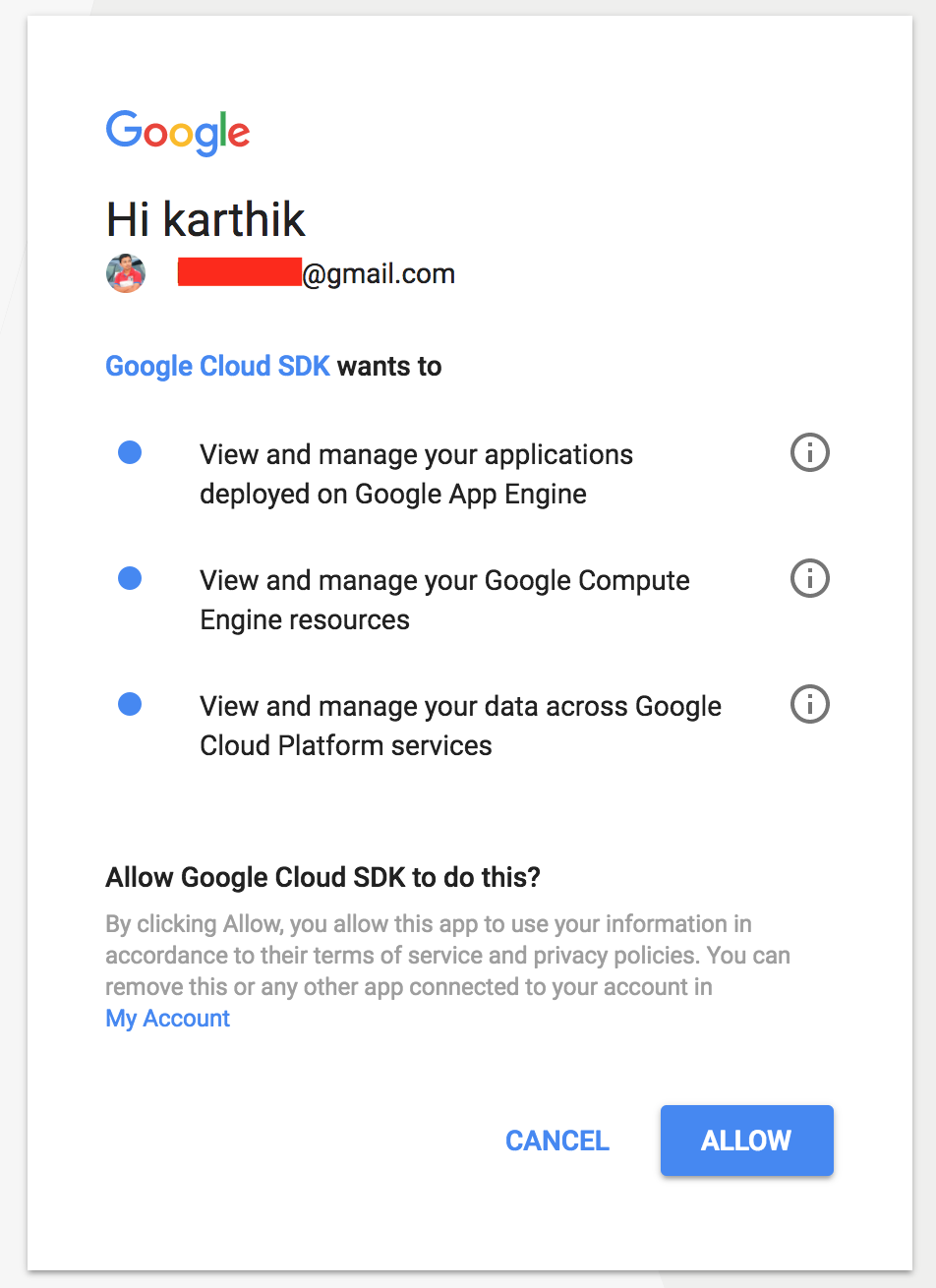
Once the Oauth process done, type the command gcloud init this will take you through the process to create and setup your Google Cloud Project. It looks something like below
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:~ karthikdivi$ gcloud init
Welcome! This command will take you through the configuration of gcloud.
Pick configuration to use:
[1] Re-initialize this configuration [default] with new settings
[2] Create a new configuration
Please enter your numeric choice: 1
Your current configuration has been set to: [default]
Choose the account you would like to use to perform operations for
this configuration:
[1] [email protected]
[2] Log in with a new account
Please enter your numeric choice: 1
You are logged in as: [[email protected]].
Pick cloud project to use:
[1] karthikdivi
[2] Create a new project
Please enter numeric choice or text value (must exactly match list
item): 1
Your current project has been set to: [karthikdivi].
Do you want to configure Google Compute Engine
(https://cloud.google.com/compute) settings (Y/n)? n
Your Google Cloud SDK is configured and ready to use!
* Commands that require authentication will use [email protected] by default
* Commands will reference project `karthikdivi` by default
Run `gcloud help config` to learn how to change individual settings
This gcloud configuration is called [default]. You can create additional configurations if you work with multiple accounts and/or projects.
Run `gcloud topic configurations` to learn more.
Some things to try next:
* Run `gcloud --help` to see the Cloud Platform services you can interact with. And run `gcloud help COMMAND` to get help on any gcloud command.
* Run `gcloud topic -h` to learn about advanced features of the SDK like arg files and output formatting
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:~ karthikdivi$
Start writing your first Google Cloud Function
Currently Google Cloud Functions are in beta and supports javascript + NodeJS platform only. So in this post we are going to create a nodeJS function and deploy it into Google Cloud Functions. First create a folder and do npm init there (You can leave all npm defaults)
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:functions karthikdivi$ mkdir hello-world
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:functions karthikdivi$ cd hello-world/
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:hello-world karthikdivi$ npm init
This utility will walk you through creating a package.json file.
It only covers the most common items, and tries to guess sensible defaults.
See `npm help json` for definitive documentation on these fields
and exactly what they do.
Use `npm install <pkg>` afterwards to install a package and
save it as a dependency in the package.json file.
Press ^C at any time to quit.
package name: (hello-world)
version: (1.0.0)
description:
entry point: (index.js)
test command:
git repository:
keywords:
author:
license: (ISC)
About to write to /Users/karthikdivi/githome/gcloud/functions/hello-world/package.json:
{
"name": "hello-world",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
Is this ok? (yes) yes
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:hello-world karthikdivi$ ls
package.json
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:hello-world karthikdivi$
Now create a file index.js and put your first function
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:hello-world kdivi$ touch index.js
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:hello-world kdivi$ vi index.js
Into the index.js file add the following content
function helloWorldFunction(req, res) {
res.send('Hello World! Yes, i am getting served from Google Cloud Functions')
}
exports.helloWorldFunction = helloWorldFunction
You are now ready with your cloud function, The only thing the above function doing is sending Hello World text in response.
Deploying the Cloud Function
You need to create a cloud storage bucket before deploying your first cloud function. You can do it by running the following command
gsutil mb gs://karthikdivi-functions-bucket/
Note: This is one time task, you can reuse the same bucket for uploading multiple functions. Now the last step for us to do is deploying our function to Google Cloud Functions. By running the following command you can deploy your function to Google Cloud Functions
gcloud beta functions deploy helloWorldFunction --trigger-http --stage-bucket karthikdivi-functions-bucket
This will deploy your local function into Google Cloud Functions, on a successful deployment you will see logs some thing like following
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:hello-world karthikdivi$ gcloud beta functions deploy helloWorldFunction --trigger-http --stage-bucket karthikdivi-functions-bucket
Copying file:///var/folders/z6/wzrgsrt92rg4xc27zr8g78xc0000gn/T/tmpWVO9xG/fun.zip [Content-Type=application/zip]...
\ [1 files][ 480.0 B/ 480.0 B]
Operation completed over 1 objects/480.0 B.
Deploying function (may take a while - up to 2 minutes)...done.
availableMemoryMb: 256
entryPoint: helloWorldFunction
httpsTrigger:
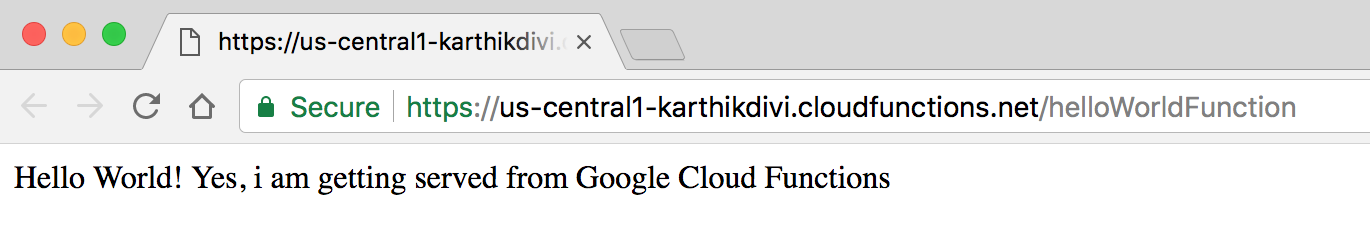
url: https://us-central1-karthikdivi.cloudfunctions.net/helloWorldFunction
labels:
deployment-tool: cli-gcloud
name: projects/karthikdivi/locations/us-central1/functions/helloWorldFunction
serviceAccountEmail: [email protected]
sourceArchiveUrl: gs://karthikdivi-functions-bucket/us-central1-projects/karthikdivi/locations/us-central1/functions/helloWorldFunction-bcyvjkhzvoqh.zip
status: ACTIVE
timeout: 60s
updateTime: '2017-12-05T17:50:48Z'
versionId: '1'
Karthiks-MacBook-Pro:hello-world karthikdivi$
Your function is ready to access now, you can get the url to trigger from the console log, look at httpsTrigger -> url and you can see https://us-central1-karthikdivi.cloudfunctions.net/helloWorldFunction is the url for our Hello World Cloud Function. If you hit this you should see the 'Hello World response' from it.